
WTF is DAT?
As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, a new phenomenon has captured the attention of investors: Crypto Treasury Funds, also known as Digital Asset Treasuries (DATs). As their name suggests, these funds accumulate and hold large amounts of crypto assets directly on their balance sheets.
While they offer indirect exposure to the high-growth potential of crypto markets, it’s essential for investors to understand their nature, benefits, and especially the risks that come with them, in order to make investment decisions.
This article dives deep into the definition, rationale, potential benefits, and detailed risks of Crypto Treasury Funds. We’ll also examine the current legal and regulatory landscape to provide a more comprehensive view of this emerging investment model.
What are Digital Asset Treasuries (DATs)?
Digital Asset Treasuries or Crypto Treasury Companies are firms whose core financial strategy involves purchasing and holding large amounts of cryptocurrencies (such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, XRP, etc.) on their balance sheets.
Their primary goal is to capitalize on the potential price appreciation of these digital assets, while offering investors an indirect way to gain exposure to the crypto market by buying the company’s stock.
Example: MicroStrategy (MSTR) is the most prominent example—a software company that has become one of the largest holders of Bitcoin in the world.
Why Are Companies Holding Crypto?
Companies are increasingly allocating cryptocurrencies to their treasuries for several strategic reasons:
- Inflation Hedge & Value Preservation: Amid rising inflation and currency depreciation, firms view crypto - especially Bitcoin - as a safe haven asset and an effective inflation hedge. They believe that crypto holds long-term value better than low-yield assets like treasury bonds.
- High Growth Potential: Compared to traditional investments, cryptocurrencies have delivered remarkable price appreciation in recent years, making them attractive options for deploying idle capital.
- Portfolio Diversification: Adding crypto to corporate balance sheets helps diversify asset holdings, reduce reliance on traditional instruments, and spread risk across different market classes.
- Lower Operational Cost: Holding crypto generally requires minimal physical infrastructure or labor costs compared to conventional business activities, making it cost-efficient.
- Market Opportunity Capture: Following the success of firms like Strategy and El Salvador, companies don’t want to miss out on this trend and are increasingly adding BTC and altcoins to their treasuries.
Structures and Operations of Crypto Treasury Funds
Crypto Treasury Funds operate under various models, but share a common purpose: to manage and optimize crypto asset exposure. Common structures include:
- Direct Holdings: The simplest form - companies purchase and hold crypto directly on their balance sheet. A prime example is MicroStrategy with its BTC reserves.
- Investment Funds: Some DATs pool capital from multiple investors and manage diversified crypto portfolios. These may take the form of hedge funds, venture capital funds, or crypto ETFs.
- Business Integration: Certain companies embed crypto holdings into their core operations - using crypto for payments, project financing, or treasury management. Tesla is a prominent example.
These funds raise capital through equity issuance, convertible debt, or other financing mechanisms. Raised funds are allocated to crypto purchases per strategic guidelines, and managed via secure storage solutions (e.g., cold wallets, multisig wallets), performance tracking, and periodic trading decisions.
How Many Companies Hold Crypto?
Before 2025, only Strategy and El Salvador were widely known for publicly buying and holding BTC in their treasuries. But in 2025, several catalysts triggered a wave of corporate crypto treasury adoption:
- Bitcoin hit new all-time highs (ATH).
- The U.S. and other nations began serious regulatory work around crypto.
- Strategy and El Salvador saw strong returns from long-term BTC dollar-cost averaging (DCA).
According to Crucible Capital's General Partner Meltem Demirors, between June and August 2025, 98 companies announced or planned to raise a combined total of $86 billion for crypto-focused treasuries.
Today, corporate interest has expanded beyond BTC, ETH, or SOL - many firms now invest in smaller-cap altcoins like HYPE, XRP, and BNB.
Risks and Challenges
Despite promising opportunities, investing in Crypto Treasury Funds comes with significant risks that investors must carefully evaluate:
- Extreme Price Volatility: Crypto prices are notoriously volatile. Sudden price swings can severely impact a company’s balance sheet and stock performance.
- Lack of Regulatory Oversight: The crypto space remains largely unregulated in many jurisdictions, exposing investors to higher risks like fraud, market manipulation, and policy shifts.
- Security Threats: Safeguarding crypto assets requires robust cybersecurity. Hacks, wallet breaches, or system failures can lead to unrecoverable losses - even with advanced protection in place.
- Limited Liquidity: Many altcoins suffer from poor liquidity, making it difficult to execute large trades without slippage - posing a challenge for sizeable treasury funds.
- Operational Risk: Crypto treasury managers may lack experience with digital asset management. Inadequate staffing or process controls can lead to poor execution and financial losses.
- Historical Returns ≠ Future Gains: Past crypto bull runs don’t guarantee future performance. The market is cyclical and prone to extended downturns.
- Valuation vs. Real Value: A key concern is whether shareholders truly receive value proportionate to the risk. Some analysts argue that buying shares in such companies may involve paying a premium just to gain indirect crypto exposure - when direct ownership might be more efficient. We'll explore this in more detail in the section below.
Digital Asset Trusts – Opportunity or a Repeat of GBTC’s Premium Trap?
Premium - A Familiar Risk in the DAT Model
One of the major concerns surrounding Digital Asset Trusts (DATs) today is the premium phenomenon - when the trading price of a DAT share on secondary markets exceeds its net asset value (NAV), which typically consists of BTC or ETH. This situation mirrors the experience of many GBTC investors, who bought in at a high premium only to find themselves “locked in” when the premium collapsed into a discount.
Take GBTC as a case study: from 2015 to 2020, it often traded at a 40 - 50% premium to NAV. However, as more transparent and liquid ETF alternatives became available, GBTC flipped to trade at a discount of up to -30%. Since GBTC did not allow investors to redeem real BTC from the trust, holders were effectively stuck with sustained losses - even if BTC itself hadn’t dropped significantly. It wasn’t until 2024, when the SEC approved GBTC's conversion to a spot ETF, that the premium fully disappeared.
Many DATs today lack a clear redemption mechanism, which raises the risk of repeating the same pattern. DAT shares could see sharp declines not because crypto assets fall, but simply because the market is no longer willing to pay a premium.
DAT Valuations and the Speculative Wave: Imitating the MicroStrategy Effect
One key reason for the rise of DATs is the strategy of raising capital to accumulate crypto at scale, thereby boosting NAV and creating the perception that their shares are “cheap” relative to spot BTC. However, this model is only sustainable if new capital continuously enters the system, willing to buy shares at ever-higher prices - a dynamic that resembles a pyramid-like investment structure.
According to Delphi Digital (July 2025), this trend is evident in several notable examples:
- Metaplanet (Japan): Holds a BTC treasury worth $2.1B, while its market cap has climbed to $4.92B, implying a 2.35x multiple.
- Bit Digital Inc.: Holds about $518M in ETH, yet its market cap has surged to $990M, or 1.9x.
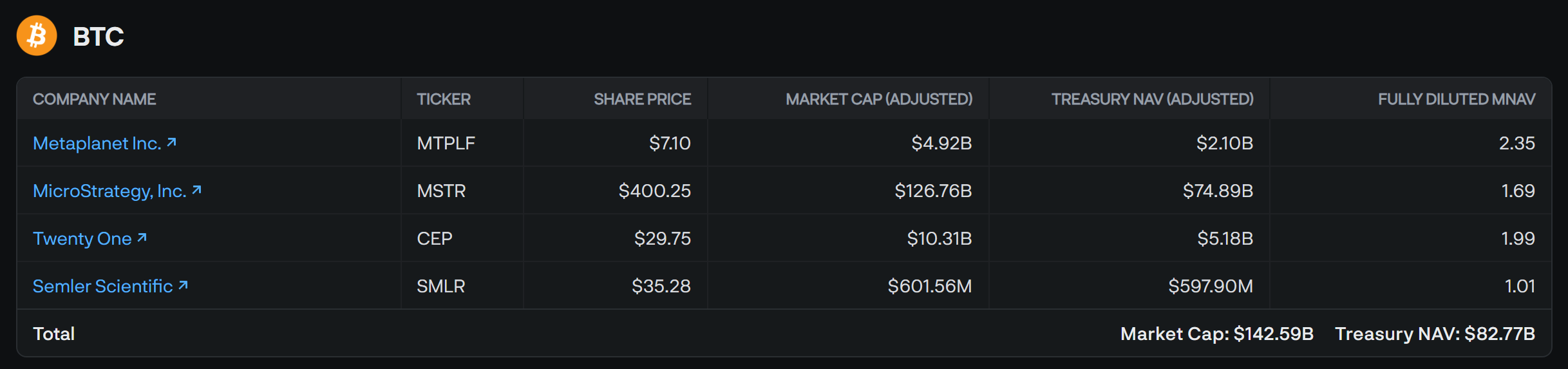
Source: https://members.delphidigital.io/data/apps/digital-asset-treasury
This phenomenon has largely been driven by the success of Strategy. Years of BTC accumulation allowed the company to realize massive gains as the market rallied, resulting in a surge in its stock price.
Many newer DATs are now replicating that strategy, under the assumption that simply holding BTC or ETH will lead to long-term stock appreciation. This is at the heart of the DAT premium speculation wave, and one that investors should approach with particular caution.
Additionally, the Premium also helps investors gauge how attractive an asset is to a fund. For example, if the market capitalization of a fund’s stock or token exceeds its NAV, it indicates strong inflows of capital — leading people to believe “the fund is hot, and buying in offers potential for further gains.” Conversely, when the Premium declines, the perceived attractiveness decreases.
Conclusion
Crypto Treasury Funds represent an exciting shift in financial markets, offering more gateways into crypto for mainstream investors. However, it’s vital to approach these instruments with balanced scrutiny and informed caution.
While they bring upside potential and diversification benefits, the embedded risks - volatility, regulatory uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and liquidity constraints - should not be overlooked.
Ultimately, understanding each fund’s operating model and risk profile, coupled with disciplined research, is key to making wise investment decisions in this fast-changing crypto landscape.


